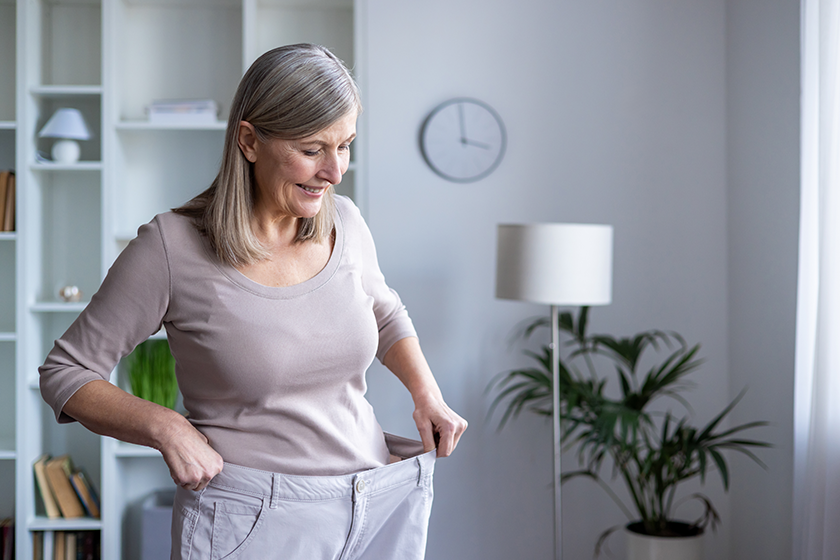
Aging brings various changes to the body, but losing weight unexpectedly is not always a normal part of growing older. If you notice a family member shedding pounds without trying, it may point to an underlying issue. Identifying the reasons behind weight loss in seniors can help you take the right steps to support their well-being.
Medical Conditions that Affect Weight
Chronic illnesses can cause the body to burn calories faster or make eating more difficult. Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, gastrointestinal disorders, and hyperthyroidism may lead to a drop in weight. If your loved one has any of these conditions, regular check-ups can help manage their effects on their body.
Cognitive diseases like Alzheimer’s can also contribute to weight loss. Forgetting to eat or being unable to recognize food can lead to reduced intake. If a family member is showing signs of confusion around mealtimes, they may need additional support.
The Role of Medications
Certain medications can impact appetite and digestion. Some drugs change the way food tastes or cause dry mouth, making meals less appealing. Others may lead to nausea, vomiting, or difficulty swallowing, discouraging regular eating.
If your loved one has started a new prescription and you notice changes in their eating habits, speak with their healthcare provider. Adjusting dosages or switching medications may help address the issue. It is important to recognize these side effects before they lead to further complications.
Mental Health and Appetite Changes
Emotional well-being has a significant impact on eating patterns. Depression and anxiety can reduce appetite, leading to weight loss over time. If your loved one appears withdrawn, uninterested in meals, or less engaged in daily activities, their emotional state might be affecting their nutrition.
Dementia and other cognitive conditions may also disrupt eating habits. Some older adults forget to eat or lose interest in food altogether. Recognizing these signs early can help you find ways to encourage proper nutrition and maintain their overall health.
Social and Lifestyle Factors
Eating habits can change due to social circumstances. Living alone, losing a spouse, or having fewer social interactions can make mealtimes feel lonely. Some older adults lose interest in preparing meals when there is no one to share them with.
Limited access to food can also contribute to weight loss. Mobility challenges, financial constraints, or a lack of transportation can make grocery shopping difficult. If a family member is struggling with these obstacles, offering assistance or finding community resources can make a difference.
Digestive Issues and Nutrient Absorption
Digestive health plays a key role in maintaining weight. Conditions such as acid reflux, ulcers, or irritable bowel syndrome can make eating uncomfortable. Some older adults may avoid certain foods due to bloating, pain, or nausea.
Malabsorption can also lead to weight loss. If the body is not absorbing enough nutrients from food, even a balanced diet may not be enough. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine if a digestive issue is affecting their weight.
Supporting Your Loved One’s Health
Addressing unexpected weight loss starts with identifying the cause. It can either stem from a medical condition, medication, or lifestyle change, and in all these, early intervention can make a significant difference. Encouraging balanced meals, regular health check-ups, and emotional support can help your loved one maintain their well-being.
If you notice concerning weight changes, do not ignore them. Seeking professional advice and making adjustments to diet, medication, or daily routines can promote healthier aging. By staying attentive, you can help your family member maintain a comfortable and nourishing lifestyle.